Over the next few weeks Unit One will share exclusive comments by Jade Marmot on the V&P film project. Today’s topic is low-cost filmmaking approaches.
To understand filmmaking a person has to watch a variety of film types. A good place to start are these four films: Citizen Kane (1941), Sweet Sweetback’s Baadasssss Song (1971), The Celebration (1998) and Sicko (2007). These go over more than 65 years. Admittedly some are more low-cost than others, with Sicko costing $9 million.
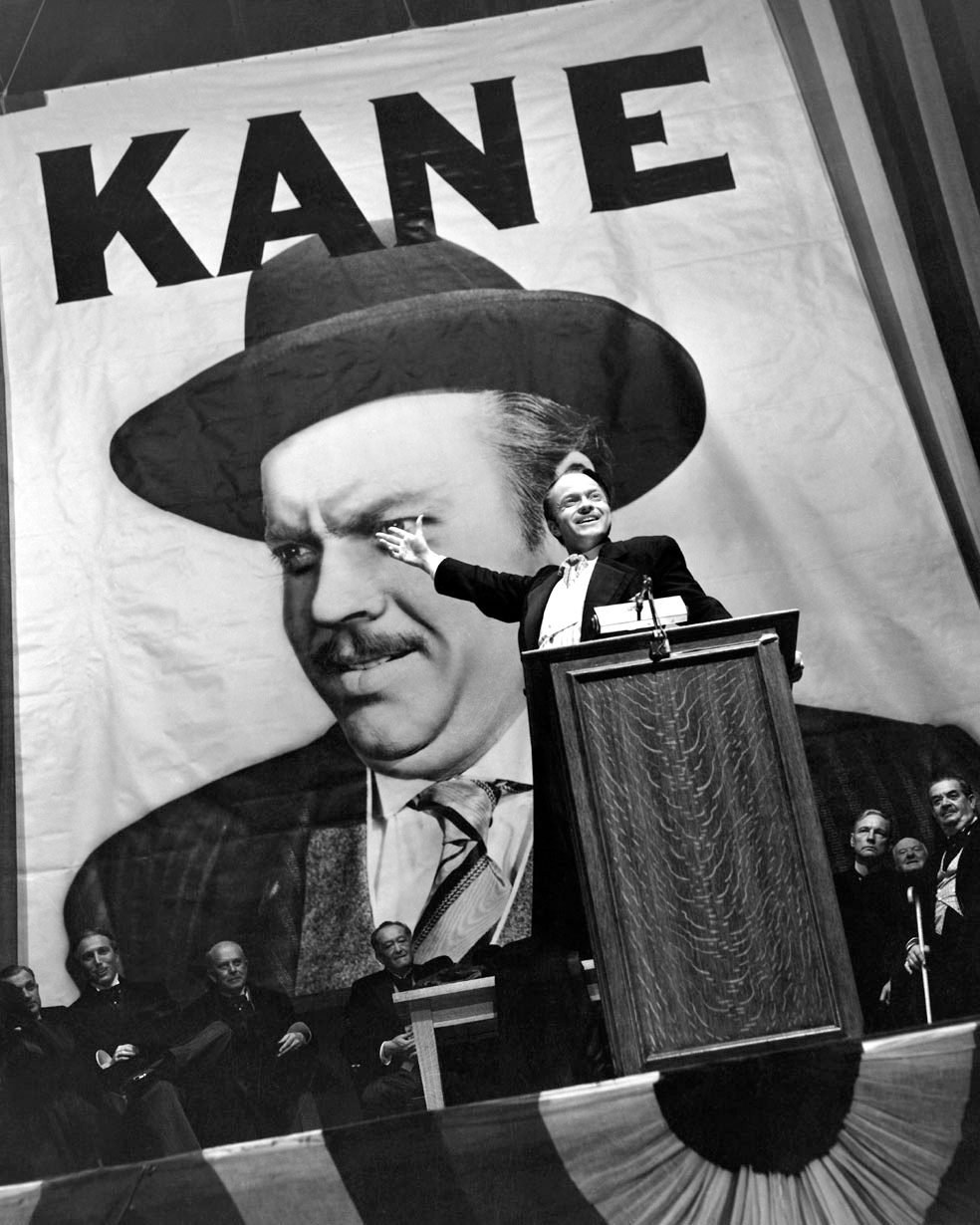
François Truffaut (1932-1984) devised auteur theory in the mid-1950s. It stated that the director was the “author” of his work. Great directors, such as Jean Renoir (1894–1979) or Alfred Hitchcock (1899-1980), have distinct styles and themes that permeate their films. While this invokes a filmmaking style that focuses on artistic intent, it concentrates on a director’s personal creative vision, denying the other participants (cast as well as crew) artistic integrity. Orson Welles’ (1915-1985) Citizen Kane (1941) is a textbook example of an auteur film. Truffaut made his feature film debut with Les Quatre Cents Coups (1959) [The 400 Blows].

In 2006 David Kipen wrote The Schreiber Theory: A Radical Rewrite of American Film History. He argues that auteur theory has wrongly skewed analysis towards a director-centred view of film. Kipen believes that the screenwriter has a greater influence on the quality of a finished work. Much of Scandinavian television production uses this approach in their 10 episode thrillers, with a number of directors being responsible for one or more of the episodes, but with a co-operating script-writing team.
Many low-budget film colleagues refer to themselves as guerrilla filmmakers. Guerrilla filmmaking involves corporate independence, low budgets, skeleton crews, and simple props. They shoot scenes quickly in real locations without permits, permission or warning. Corporate independence means that the filmmakers are not accountable to anyone but themselves.
“Guerrilla filmmaking is driven by passion with whatever means at hand”, said Mark Hill, Yukon Film Commission Manager. Guerrilla filmmaking focuses too much on technique, rather than on content. For pacifists, there are also problems with the military connotations of the title. Film critic Roger Ebert described Sweet Sweetback’s Baadasssss Song (1971) written, produced, scored, directed by, and starring Melvin Van Peebles (1932-), as “a textbook on guerrilla filmmaking.” If you cannot find this film, an equivalent example is Robert Rodriguez’ (1968-) El Mariachi (1992). It cost about $7,000 to make, with money partially raised by volunteering in medical research studies. While originally intended for the Spanish-language low-budget home-video market, it received international distribution. Rodriguez described his filmmaking experiences in his book Rebel Without a Crew. The book and film continue to inspire filmmakers to make no-budget films.

The Dogme 95 approach to filmmaking turns auteur theory upside down. It codifies filmmaking in a 10-point Vow of Chastity written by Lars von Trier (1956-) and Thomas Vinterberg (1969-) that prohibits expensive and spectacular special effects, post-production modifications and other technical ploys. Filmmaking concentrates on content: the story and actors’ performances. Here the director is a nameless servant; at best a coordinator. One of the most powerful films is Vinterberg’s Festen (1998) [The Celebration]. Note: It can be a bit too powerful for people with assorted family issues that can be triggered. For those people Italiensk for begyndere (2000) [Italian for Beginners] a Danish romantic comedy, written and directed by Lone Scherfig (1959-) is more appropriate.

Political cinema may refer to films that do not hide their political stance, but this does not mean that they are pure propaganda. Most films are political, including escapist films offering entertainment. In Nazi Germany, the authorities organized a large production of deliberately escapist movies. Today, Hollywood cinema misrepresents black, women, gays, working-class people, and others frequently in the form of stereotypes. Michael Moore (1954-) is one of many political filmmakers, with Sicko (2007) being one of his most popular, and lucrative. It investigates American health care, with a focus on health insurance and pharmaceuticals. The movie compares the for-profit, non-universal U.S. system with the non-profit universal health care systems of Canada, the United Kingdom, France and Cuba. Moore rejects the label of political activism as redundant in a democracy, “I and you and everyone else has to be a political activist. If we’re not politically active, it [presumably USA] ceases to be a democracy.”
That’s it for today!
Come back next time, when Jade Marmot writes about the institution of cinema itself, and its mission to pacify spectators, and how Joyful Marmot Productions aims to change this. Until then, think about the cinema, and how people congregate but do not to act together or to talk to each other, but sit silently, and isolated from each other.